ABOUT HEART DISEASE
We all want to age well, but far too many young Americans are having heart attacks or strokes and many are life-ending events. In fact, someone in the U.S. has a heart attack every 43 seconds.
Heart disease and stroke are not only the leading causes of death but can make it impossible for some adults to return to work and enjoy their favorite activities. According to the Center for Disease Control, there are more people under age 65 who are dying from preventable heart disease and strokes than those who are older than 65 years. Once thought to be a “man’s disease”, heart attacks and strokes kill more women each year than the next four causes of death combined, including cancer.
UNDERSTANDING YOUR RISK
The inner lining of your arteries are damaged by things like smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and poor lifestyle habits. This damage allows cholesterol in your blood to more easily enter the walls of your arteries, leading to disease.
INFLAMMATION AND HEART DISEASE
Cleveland HeartLab’s inflammation tests can help YOU and your doctor have a better understanding of YOUR RISK of heart attack or stroke.
Watch the Know Your Risk Video™ to learn more about how simple blood and urine tests help doctors assess inflammation so they have a more complete picture of your individual risk for a heart attack and stroke. Understand how doctors identify which patient is at risk based on inflammation test results.
INFLAMMATION TESTING
Cholesterol testing provides part of the picture. Inflammation testing provides a more complete picture of YOUR RISK for heart disease.
Cleveland HeartLab offers simple blood and urine testing that provides you and your doctor information that may be used to help evaluate your risk for heart disease. These tests can be used alongside cholesterol testing to provide a more complete picture of YOUR RISK for heart disease.
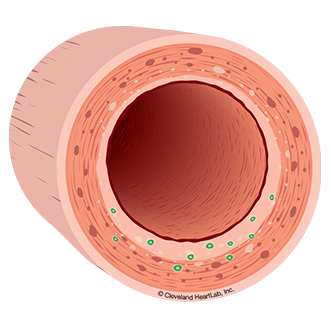
The following tests may help to identify your early risk for disease:F2-Isoprostanes (F2-IsoPs) is a 'lifestyle marker' that measures the amount of oxidation in your body that may damage your endothelium. Eating too much red meat, smoking or not exercising enough can increase your F2-Isoprostanes levels and increase your risk for future heart disease. Oxidized LDL (OxLDL) is a marker that measures the amount of LDL - or "bad cholesterol"- that has been damage due to oxidation. Poor lifestyle habits can increase your OxLDL levels and increase your risk for pre-diabetes.
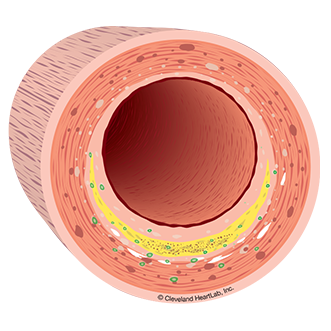
The following tests may help to identify the presence of disease:hsCRP is a general marker of inflammation. The presence of a cold may increase hsCRP levels over the short-term (days to weeks). However, the accumulation of cholesterol in the artery wall many result in increased hsCRP levels over the long-term (years to decades). Urinary Microalbumin is a marker of endothelial damage in your kidneys. If the endothelium is damaged in your kidneys then it’s likely damaged in other parts of your body including your arteries. Increased levels of urinary microalbumin may identify the presence of diabetes or heart disease.
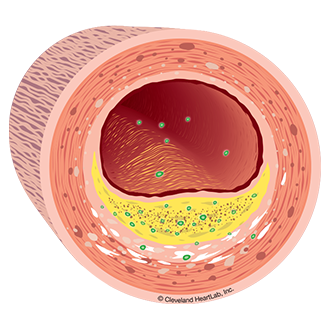
The following tests may help to identify active disease:
Lp-PLA2 Activity is a marker that measures the active build-up of cholesterol inside your artery walls. Your risk for a heart attack or stroke increase as Lp-PLA2 Activity levels increase.
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a marker that measures the body's response to a damaged endothelium that has become thinned, cracked and ultimately unstable due to cholesterol accumulation and inflammation. Your risk for a heart attack increases as your MPO levels increase.

F2-IsoPs
Information about the inflammation test for
F2-Isoprostanes (F2-IsoPs).
Microalbumin
Information about the inflammation test for
Urinary Microalbumin.
OxLDL
Information about the inflammation test for
Oxidized LDL (OxLDL).
MPO
Information about the inflammation test for Myeloperoxidase (MPO).
hsCRP
Information about the inflammation test for
High-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP).
Lp-PLA2 Activity
Information about the inflammation
test for Lp-PLA2 Activity.
ARE YOU AT RISK?
Often the first symptom ofheart disease is a heart attack.
Ultrasound and imaging tests help doctors identify patients at risk for a heart attack but they cannot be done everywhere and are too expensive to be done on everyone. Fortunately there are new blood and urine tests that are easy to do in your doctor’s office. These simple tests can help you and your doctor know your risk for a heart attack or stroke. When you KNOW YOUR RISK of a heart attack or stroke, you can work with your doctor to REDUCE YOUR RISK.
Age – Your risk increases as you get older.
Gender – Men are at higher risk if over 45 years of age and women if over 55 years of age.
Family History – Your risk is higher if members of your family have had cardiovascular disease (heart attack, bypass surgery, a stent, or stroke) at a young age; before age 55 years for men or before age 65 years for women.
High Blood Pressure – Know your blood pressure. Ideally it should be less than 120/80 mm Hg when you are at rest, although somewhat higher levels are often OK with your doctor when you’re older.
High Blood Cholesterol – Your risk for heart attack is lower if your LDL-cholesterol is less than 100 mg/dL and your non-HDL-cholesterol is less than 130 mg/dL.
Physical Inactivity – Sitting for long periods of time increases your risk. Even moving around for 5-10 minute periods throughout the day can lower heart attack risk.
Obesity and Overweight – Risk for disease is related to those extra pounds around your waist line. Losing 5-10% of your body weight reduces health risk.
Smoking – Research has shown that every 5 cigarettes a day smoked increases heart attack risk. Quitting smoking reduces heart attack risk immediately.
Diabetes – It is very important to KNOW your blood sugar level. Normal blood sugar levels are under 100 mg/dL.
LOWER YOUR RISK NOW


 The blood vessels that feed your heart muscle and brain are called arteries. These arteries carry blood that is the “fuel supply” you need for life. The arteries that feed the heart muscle are called coronary arteries and provide blood to the heart muscle so that it can pump blood. When cholesterol and inflammation build up within the walls of your coronary arteries, it’s called coronary artery disease.
The blood vessels that feed your heart muscle and brain are called arteries. These arteries carry blood that is the “fuel supply” you need for life. The arteries that feed the heart muscle are called coronary arteries and provide blood to the heart muscle so that it can pump blood. When cholesterol and inflammation build up within the walls of your coronary arteries, it’s called coronary artery disease.
 A heart attack can occur when a coronary artery becomes blocked and blood can no longer get through to feed the heart muscle. The blockage is caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the wall of the artery (plaque with a large lipid core) that becomes inflamed and then ruptures or breaks open causing a clot to form. It’s similar to having a sore or pimple on the inside of your artery wall. If there is a lot of cholesterol and inflammation in the plaque, the cap on the sore can become very thin and weak (unstable). If the thin cap is damaged and the inflamed sore breaks open, your body tries to repair the damage by forming a clot. The combination of the plaque and clot together can completely close off the coronary artery and cause a sudden heart attack or sudden death. If this process happens in an artery that brings the blood supply to your brain, a stroke can occur.
A heart attack can occur when a coronary artery becomes blocked and blood can no longer get through to feed the heart muscle. The blockage is caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the wall of the artery (plaque with a large lipid core) that becomes inflamed and then ruptures or breaks open causing a clot to form. It’s similar to having a sore or pimple on the inside of your artery wall. If there is a lot of cholesterol and inflammation in the plaque, the cap on the sore can become very thin and weak (unstable). If the thin cap is damaged and the inflamed sore breaks open, your body tries to repair the damage by forming a clot. The combination of the plaque and clot together can completely close off the coronary artery and cause a sudden heart attack or sudden death. If this process happens in an artery that brings the blood supply to your brain, a stroke can occur.